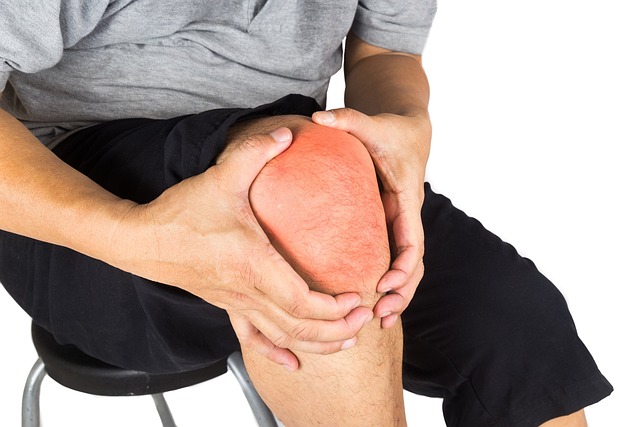
Swollen legs, or leg edema, can be a symptom of various underlying health issues. This condition can range from mild and temporary to severe and chronic, significantly impacting an individual’s mobility and quality of life. Understanding the causes of leg swelling is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. This detailed guide explores the common and less common causes of swollen legs, their symptoms, and potential treatments.
Common Causes of Swollen Legs
1. Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Overview: One of the most common causes of swollen legs is prolonged periods of standing or sitting. Gravity causes blood to pool in the lower extremities, leading to fluid accumulation in the tissues.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the lower legs and ankles
- Feeling of heaviness or discomfort
- Swelling that subsides with movement or elevation
Prevention and Treatment:
- Take breaks to move around and stretch every hour
- Elevate legs when sitting or lying down
- Wear compression stockings to improve circulation
- Avoid crossing legs when sitting
2. Varicose Veins
Overview: Varicose veins occur when veins become enlarged, twisted, and unable to effectively return blood to the heart, causing blood to pool in the legs.
Symptoms:
- Visible, bulging veins
- Aching or throbbing pain in the legs
- Itching around the veins
- Swelling, especially after long periods of standing
Prevention and Treatment:
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting
- Wear compression stockings
- Elevate legs when possible
- Medical treatments include sclerotherapy, laser treatment, or surgery
3. Heart Failure
Overview: Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid buildup in the legs and other parts of the body.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and weakness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Treatment:
- Medications to improve heart function and reduce fluid buildup (diuretics)
- Lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise
- Monitoring and managing underlying heart conditions
- In severe cases, surgical interventions or devices like pacemakers
4. Kidney Disease
Overview: Kidney disease can cause fluid retention in the body, leading to swelling in the legs. When kidneys are not functioning properly, they cannot remove excess fluid efficiently.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Changes in urine output and appearance
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
Treatment:
- Medications to manage underlying kidney conditions
- Dietary changes to reduce sodium and fluid intake
- Dialysis in advanced cases
- Monitoring and managing blood pressure and diabetes
5. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Overview: DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. This can cause significant swelling and can be life-threatening if the clot travels to the lungs.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in one leg (typically)
- Pain and tenderness in the affected leg
- Warmth and redness in the leg
- Enlarged veins visible under the skin
Treatment:
- Anticoagulant medications to prevent clot growth and new clots
- Compression stockings to reduce swelling
- Elevating the leg to improve blood flow
- In severe cases, surgical intervention to remove the clot
6. Lymphedema
Overview: Lymphedema is a condition where the lymphatic system is damaged or blocked, leading to the accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues.
Symptoms:
- Persistent swelling in the legs, feet, or toes
- Heaviness or tightness in the affected area
- Recurrent infections
- Thickening or hardening of the skin (fibrosis)
Treatment:
- Manual lymph drainage (massage)
- Compression garments to promote fluid movement
- Exercise to stimulate lymphatic flow
- In severe cases, surgery to remove excess tissue or create new drainage pathways
Less Common Causes of Swollen Legs
1. Liver Disease
Overview: Liver disease, such as cirrhosis, can lead to fluid retention and swelling in the legs due to impaired liver function and reduced albumin production.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Fatigue and weakness
Treatment:
- Medications to manage liver disease and symptoms
- Dietary changes to reduce sodium and fluid intake
- Monitoring and managing underlying conditions like hepatitis or alcoholism
- In severe cases, liver transplantation
2. Infections
Overview: Infections, particularly cellulitis, can cause inflammation and swelling in the legs. Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that requires prompt medical treatment.
Symptoms:
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area
- Pain and tenderness
- Fever and chills
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Treatment:
- Antibiotic medications to treat the infection
- Elevation of the affected leg
- Keeping the skin clean and moisturized to prevent future infections
- Hospitalization in severe cases
3. Medications
Overview: Certain medications can cause fluid retention and swelling in the legs as a side effect. Common culprits include corticosteroids, hormone replacement therapy, and some blood pressure medications.
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Weight gain
- Other side effects specific to the medication
Treatment:
- Discussing medication adjustments with a healthcare provider
- Monitoring and managing side effects
- Lifestyle changes to reduce fluid retention, such as reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild swelling in the legs can often be managed with home remedies and lifestyle changes, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent swelling
- Swelling accompanied by pain, redness, or warmth
- Sudden onset of swelling in one leg
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Signs of infection, such as fever or chills
Swollen legs can result from a variety of causes, ranging from simple lifestyle factors to serious medical conditions. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and management. Maintaining good circulation through regular movement, wearing compression stockings, and managing underlying health conditions can help prevent and reduce leg swelling. If you experience persistent or severe swelling, it is important to seek medical advice to rule out serious conditions and receive appropriate treatment. By understanding the diverse factors that contribute to leg edema, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and maintain healthy, active lives.